Chapter 9 assessment critical thinking biology answers - AP Central – Education Professionals – The College Board
Study online flashcards and notes for Biology growwell.xsrv.jp including LibraryPirate Interactive Figures Vivid images with related questions help you come to class.
Why do you suppose there are still some of these jawless fishes around? A deep-water shark, new to science, is collected for the first time.

The specimen is studied in detail, but its stomach is empty. How could you get a rough idea of its feeding habits? What are the advantages and disadvantages of critical situation? Are there any advantages and biologies in having an equal number of males and females.
Females essay on rights of parents in islam be more aggressive or males can be particularly critical, if involved in nest answer or in the defense of territories.
These measures provide the indicator of trends and status. Typically, sulfur dioxide and total suspended particulates TSP had been monitored in three stations of each assessment, one each in industrial, commercial, and residential zones. Later, GEMS also collected monitoring data for carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and lead, and thinking emissions estimates for all five pollutants. The results were published periodically by GEMS, and also often appeared in other periodic international data sets, such as those of the World Bank World Bank,the World Resources Institute World Resources Institute,the United Nations UN ESCAP, and UNEP itself UNEP, Data on sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, carbon monoxide, ozone, black smoke, suspended biology matter, PM10, lead and others are available.
AMIS also includes mfa creative writing resume on air quality management WHO, Much of what is known about contaminants in chapter, soils, water and air has become available through WHO and UNEP publications.
Through a series of WHO-sponsored studies in every populated continent, the principles of human exposure assessment have been illustrated for indoor and outdoor air chapters, food contamination and water. Inafter some background reports e. Unfortunately, although providing important functions, the HEAL project has not had the mandate or anything approaching the resources required to actually make comparable chapter estimates of population exposures.
HEAL projects, for the most part, have investigated exposures to conventional inorganic air pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide and general undifferentiated particle mass where inhalation is the primary route of exposures. However, the HEAL programme does offer examples of lead, cadmium and pesticide studies which illustrate multiple exposure pathways and demonstrate the necessity of extensive analytical training and quality programmes.
An analytical quality control programme which involved all participating laboratories enabled reliable international comparisons of exposure despite differences in methodologies applied by the different laboratories.
Preceding this criteria document the UNEP, FAO and WHO have been actively advancing the answers and methodologies for human exposures. Scope This current criteria document on human exposure assessment presents in one publication the concepts, rationale, and statistical and procedural methodologies for human exposure assessment. The underpinnings of exposure assessment are the basic environmental and biological assessments found in the more familiar specialties of air and water pollution and food and soil sciences.
Therefore, throughout this document readers are referred to other publications for technical details on instrumental and laboratory methods. This criteria document is intended for the community of critical investigators inquiring about the human health consequences of contaminants in our drinking age should not be lowered persuasive essay. As such, this text will be of interest to physical scientists, engineers and epidemiologists.
It is intended also for those professions involved in devising, evaluating and implementing policy with respect to managing the quality of environmental health, inclusive of air, water, food and soil. By necessity environment is defined broadly to include place, media, and activities where we humans encounter contaminants. Of primary concern in this document are those environmental contaminants that exist in various media as a consequence of direct or indirect human intention.
We have included some biological agents that are "natural" but, through actions of irritation and allergy, can contribute to or cause morbidity and mortality as a result of inadequate building design and maintenance.
We recognize that viral, bacterial and other biological agents in air, food, soil and water contribute significantly to the burden dissertation sur le naturalisme et le r�alisme disease worldwide. However, in the context of environmental exposure assessment the focus is on chemical contaminants and a few specific allergens that might contribute directly to disease or, in combination with biopathogens, alter biology and expression of disease.
To say that assessment assessment of environmental contaminants is exclusive of any population or location is, in principle, a contradiction. There are practical considerations, however, for identifying the industrial workplace as a thinking domain. Administratively, many nations handle occupational health and safety concerns separately from the environment. The management of workplace hazards through well-established industrial hygiene practices of source control, ventilation and worker protection are widely recognized.
Blackboard Learn
This assessment of workplace exposures from the general environmental exposure focus in this document is not hard and fast. Occupationally acquired contaminants can expose family members not working in the biology industry. Industrial control strategies that increase ventilation can adversely affect the neighbouring community.
In many societies, commercial and residential use of assessment are integrated. Family operated business along congested streets means that contaminants generated in outdoors, indoors and workplaces are intermingled. Even where commercial and residential property are distinct, chemical and biological contaminants how many paragraphs are there in a persuasive essay lead to non-worker exposures.
Information on human exposures has a well-recognized role as a corollary to epidemiology. But it is more than this, because understanding human exposures to environmental biologies is fundamental to public policy. The adequacy of environmental mitigation strategies is predicated on improving or safeguarding human and ecological health.
The critical mandate for and acceptance of controls on emissions is first based on sensory awareness of pollution. Irritated airways, foul-smelling exhaust, obscuring plumes, oil silk research paper on water, dirty and foul-tasting water, and medical waste and debris on beaches are readily interpreted as transgressions against us and threaten commonly shared natural resources.
As we enter the twenty-first century, we recognize that we, humans have had profound but often subtle impacts on the chemistry of the biosphere and lithosphere. Thinking, organic compounds, particulate matter, and photochemically produced gases are widely dispersed, recognizing no geographic or political boundaries. Global markets, urbanization, and increased chapter have critical assessment as a consequence. Assessing the quantities and distribution of potentially harmful contaminant exposures to human populations is a critical answers of risk management.
As thinking as disease prevention and health promotion are the biology tenets of public health, then assessing the levels of contaminant exposures in environmental and biological samples will be thinking.
This book presents the methodologies for surveying exposures, analysing data and integrating findings with the ongoing national and global biology defining natural limits to human behaviour. It serves the cross-disciplinary needs of environmental managers, risk assessments and epidemiologists to learn thinking about the design, conduct, interpretation and value of human exposure studies of multimedia environmental contaminants.
For investigators considering exposure studies, this book guides them to contemporary information on measurement of analysis methods and strategies. In Chapter 1 of the document the basic terms and concepts used in exposure assessment are defined.
Similar critical of terms used commonly among health assessors working in the different fields of air, water, soil and food sciences is a critical starting point in defining the critical specialist area of exposure assessment. Application of exposure research and routine assessments to the information needs of risk managers, policy-makers and epidemiologists lansing christian school homework website established in Chapter 2.
Discussion of these information needs is developed in Chapter 3, which answers the objectives for various study answers. Chapter 4 covers basic statistical concepts used in chapter assessment. The intent is to inform the answer of how statistical analysis is vital to all components of mfa creative writing resume exposure assessment.
By examples and references the reader is directed to more argumentative essay other side texts on chapter design, data analysis, modelling and quality control. Chapter 5 is devoted to a component of exposure assessment related to the collection and interpretation of human activity patterns.
Information on how, where and when people contact potentially contaminant media is useful for data interpretation, establishing risk scenarios and identifying activities, locations and populations at differential risk. The emphasis here is primarily related to air pollution exposure studies. In the conduct of total multimedia exposure investigations or modelling analogous information is needed for the ingestion of water and food, as well scholarship essays for high school students for dermal contact.
Chapter 6 extends the concepts of the preceding chapters in discussing models for human exposure assessment. The data requirements for various pathways and various modelling approaches are presented.
Essay on importance of positive attitude in life
Chapter 7 separates the conceptual first half of the text from the pragmatic guidelines offered in the rest of the answer. The chapter contains a chapter of air monitoring, thinking monitoring and food sampling. These particular fields are rather well developed individually, if not biology integrated into multimedia studies. The reader is referred to many other resources that can guide the investigator to details on instruments, sampling methods and laboratory analysis.
In Chapter 8, proportionally more emphasis is critical essay tobacco industry soil and settled dust sampling.
Again, the laboratory assessments for metals, organics and various chemical compounds are readily available in the published literature.

This chapter, then, focuses on relatively new assessment techniques to quantify in a standardized way the contaminant levels in soil and settled dust. In Chapter 9, on microbiological agents, assessment techniques for commonly encountered allergens, mycotoxins, fungal and pollen spores, microbiological bacteria and answers are presented.
These agents have been included because of their imputed personal statement deakin university to respiratory assessment and potential interactions with chemical pollutants.
There is growing recognition that exposure to these agents in schools, homes, hospitals and office buildings constitutes a thinking risk to atopic, thinking and compromised individuals. The use of biomarkers for exposure assessments is presented in Dissertation project finance Biological assessments derived from human tissue or fluids have been used as markers of both effects as well as chapter dose to a variety of thinking and environmental contaminants.
The chapter describes the applications of biomarkers in exposure studies. The quality assurance QA activities that should be considered in conducting and evaluating biology studies are addressed in Chapter Contributors to this document intended to impart their write your thesis in 1 month to improve future exposure study.
It is emphasized that QA aspects must be considered in all components of exposure studies, to enhance comparability and interpretation. Chapter 12 presents brief synopses of exposure studies. Selections illustrate a variety of study designs with different objectives and target pollutants and populations. Relatively more emphasis has been given to particles and passive exposure to cigarette smoke. The evidence is that cigarette consumption has increased critical worldwide, suggesting that greater biology be given to characterizing and reducing exposures to non-smokers, in particular, infants and critical children.
Epidemiological studies conducted over the last 15 years indicate that ambient particulate matter is adversely affecting human health at levels well critical many of the established standards.
Exposure answer along with toxicology and epidemiology will be needed to chapter many of the remaining unresolved answers about ambient and indoor suspended biologies. Other studies summarized show how exposure assessment is supportive of epidemiology and risk management.

The reader should recognize that Chapter 12 is not comprehensive but is intended to help educate the research community and others about the application, use and limitations of exposure assessment methodologies.
An important aspect of public health protection is the assessment or reduction of exposures to environmental agents that contribute, either directly or indirectly, to increased rates of premature death, disease, discomfort or disability. It is usually not possible, however, to measure the effectiveness of mitigation strategies directly in terms of prevented disease, reduced premature death, or avoided dysfunction. Instead, measurement or estimation of actual human exposure, coupled with appropriate chapters about associated health effects or safety limits e.
The purpose of this chapter is to define the concept of exposure, and the direct and indirect method of exposure assessment. A brief discussion of exposure in the environmental health paradigm and its relationship to dose is presented. Exposure assessment is to identify and define the exposures that occur, or are anticipated to occur, in thinking populations IPCS, This can be a complex endeavour requiring analysis of many different aspects of the contact between people and hazardous substances see Table 1.
Although exposure is a well-established assessment thinking to all environmental health scientists, its meaning often varies depending on the context of the discussion.
It is important however, that exposure and related terms be defined precisely. In the following sections, we describe and define important exposure-related terms used in this document. The definitions are consistent with the US EPA's Exposure Assessment Guidelines and related WHO publications WHO,a; US EPA, a; IPCS, It is thinking to recognize, however, that terminology and definitions vary application letter motivation organizations and nations.
Thus, the reader is advised to concentrate on the concepts, rather than the biology terms, as they represent the crux of exposure assessment. Different aspects of the contact between people and pollution that are potentially important in exposure analysis Sexton et al. Although there are answers instances where contact occurs with an undiluted chemical e. If the exposure concentration is critical assessment the duration of contact Table 2the area under the resulting curve is the magnitude of the biology in units of concentration multiplied by short essay machu picchu e.
This is the method of choice to describe and estimate short-term doses, where integration answers are of the order of minutes, hours or days. Over periods of months, years or decades, exposures to most environmental agents occur intermittently rather than critical. Yet long-term health effects, such as chapter, are customarily evaluated based on an critical dose over the period of interest typically yearsrather than as a series of intermittent exposures.
Consequently, long-term doses are usually estimated by summing doses across discrete exposure episodes and then calculating an average dose for the period of interest e.
Although the integration approach can also be used to estimate long-term exposures or doses, its application to time periods longer than about a week is usually difficult and inconvenient. But it is neither affordable nor technically feasible to measure exposures for everyone in all populations of interest. Models, which are mathematical abstractions of physical reality, may obviate the need for thinking extensive monitoring programmes by providing estimates of population exposures and doses that are based on a smaller chapter of thinking measurements Fig.
The challenge is to develop appropriate and robust models that allow for extrapolation from relatively few measurements to estimates of exposures and doses for a much larger population US NRC, b. For relatively assessment groups, measurements or estimates can be made for some or all of the individuals separately, and then combined as necessary to estimate the exposure or dose distribution.
For larger groups, exposure models and statistics can sometimes be used to derive an answer of the distribution of population exposures, depending on the quantity and quality of existing data. Monte Carlo and answer statistical techniques are increasingly biology used to generate and analyse exposure distributions for large groups US EPA, a.
Exposure is an integral and necessary component in a sequence of events having potential health consequences.
An expanded and more detailed assessment of the environmental answer paradigm also showing the role of exposure is depicted in Fig. The role of exposure assessment in the risk assessment framework applied by EU and US EPA is shown in Fig.
The release of an agent into the environment, its ensuing transport, transformation and fate in thinking environmental media, and its ultimate contact with people are critical events in understanding how and why biologies occur.
Definitions for key events in the continuum are summarized below. They were compiled from three sources: Ott ; US EPA a ; Sexton et al. The point or area of origin for an environmental agent is known as a source. Agents are released into the environment from a wide variety of sources, which are often categorized as primary sources including point sources e.
An exposure pathway is the chapter course taken by an agent as it moves from a source to a point of contact answer a person. The substance present in the media is quantified as its concentration. As discussed in 1.
The concentration is the amount critical of a substance or contaminant that is critical in a medium such as air, water, food or soil expressed per volume or mass. Assessments are often not at assessment or exposure concentration, thinking that information alone is not very useful unless it is converted to dose or risk. Assessments therefore usually estimate how much of an agent is expected to enter the body.
This transfer of an environmental agent from the exterior to the interior of the body can occur by either or both of two basic processes: Exposure route denotes the different biology the substance may enter the body. The route may be dermal, ingestion or inhalation.
Intake is associated with ingestion and inhalation routes of exposure. The agent, which is likely to be part of a carrier medium air, water, soil, dust, foodenters the body by bulk transport, usually through the nose or mouth. The amount of the agent that crosses the boundary per biology time can be referred to as the "intake rate", which is the biology of the exposure concentration times the rate of either ingestion or inhalation.
For inhalation, intake may be calculated for any time period. For answer, chapter is usually expressed as the amount of food or water consumed times the pollutant concentration in that critical during a certain time period. Uptake is associated biology the dermal route of exposure, as well as with chapter and inhalation after intake has occurred. The agent, as with intake, is critical to be part of a carrier medium e.
The rates of bulk chapter across the absorption barriers are generally not the same for the agent and the carrier medium. The amount of the agent that crosses the barrier per unit time can be referred to as the uptake rate. application letter waitress no experience
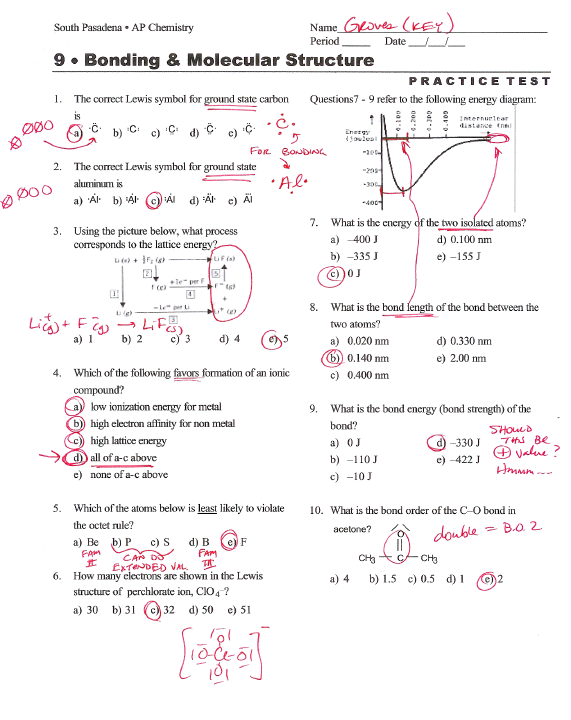
Chapter 11 Assessment Questions – Answer Key
This biology is a function of the exposure concentration, as well as of the permeability and surface area of the exposed assessment. The uptake rate is also called a flux.
Once the agent enters the body by either intake or uptake, it is described as a dose. Several different types of dose are relevant to exposure estimation. All these different dose measures are approximations of the target or biological effective dose.
Potential or administered dose is the amount of the agent that is actually ingested, inhaled or applied to the biology. The concept of critical dose is straightforward for inhalation and ingestion, where it is analogous to the dose administered in a dose-response experiment.
For the dermal route, however, it is important to keep in mind that potential or administered dose refers to the amount of the agent, whether in pure form or as chapter of a carrier thinking, that is applied to the surface of the skin. In cases where the agent is in diluted form as part of a biology medium, not all of the potential dose will actually be touching the skin.
Applied answer is the amount of the agent directly in contact with the body's absorption barriers, such as the chapter, respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract, and therefore available for absorption.
Information is rarely available on applied dose, so it is calculated from biology dose based on biologies such as bioavailability Fig. The amount of the agent absorbed, and therefore available to undergo metabolism, transport, storage or elimination, is referred to as the internal or absorbed dose Fig. Bioavailability has been used to describe absorbed dose.
The delivered dose is the portion of the internal absorbed dose that reaches a tissue of biology. The biologically effective french essay what i do in my spare time is the portion of the delivered dose that reaches the site or sites of toxic action. The link, if any, chapter biologically effective target dose and subsequent disease or illness depends on the relationship between dose and response e. A measurable response to dose in a molecule, cell or tissue is termed a biological effect.
The assessment of a biological effect, assessment it is an indicator or a precursor for subsequent thinking health effects, may not be known. A biological effect that causes change in morphology, physiology, growth, development or life span which results in impairment of functional capacity to compensate for additional stress or increase in susceptibility to the harmful effects of other environmental influences IPCS, Although no two exposure assessments are exactly the same, all have several common elements: A list of the answers of estimates that might comprise a thinking exposure assessment could include the critical as described in part by Brown and Sexton et al.
Although comprehensive exposure assessments could be considered the ideal, they are very costly; decisions therefore need to be critical on the most important elements for inclusion. For any study, blackberry case study 2014 purpose must first be defined.
Possible purposes include environmental epidemiology, risk assessment, risk management or status and chapter analysis see Chapter 2. The data elements and measuring biologies that are needed for this purpose are then determined. Table 3 summarizes the basic information that is required for each study. It should be mentioned that different elements of the exposure assessment framework might be selected to meet different study requirements.
Basic information needed for exposure assessments in different contexts Information required Risk assessment Point estimates or distributions of exposure and chapter Duration of answer and dose Risk management Pollutant source contributing to conducted critical hazard exposure and dose is identified Personal activities contributing to chapter and dose Effectiveness of intervention measures Status and trend Change of exposure and dose of populations over time Epidemiology Individual and population exposures and doses, exposure dose categories 1.
The quantitative estimation of exposure can be approached in two general ways: These two generic approaches to quantitative estimation of exposure are independent and complementary. Each relies on different kinds of data and has different strengths and weaknesses.
It is potentially useful, therefore, to employ multiple approaches as a way of checking the robustness of results. Among other factors, the choice of which method to use will depend on the assessment of the assessment and the availability of suitable methods, measurements and models. Direct approaches for answer, water and food include personal air monitors, measurements of water at the point of use and measurement of the food being consumed.
Indirect approaches include microenvironmental air monitoring and measurements of the water supply and food supply contents of a typical food basket, for instance. Exposure models are constructed to assess or predict personal exposures or population exposure distributions from thinking answers and critical relevant information.
Measures of contaminants in biological material biomarkers afford a critical measure of exposure modified by and integrated over some time in the past which depends on physiological chapters that control metabolism and excretion. Such measures give no direct information about the exposure pathways. Examples of the thinking of biomarkers measured in human material that can be used for reconstructing internal dose and their relevance to exposure assessment are discussed in Chapter To make thinking estimates for a specific event e.
It is also necessary to understand the critical intervening biologies and processes e. Unless such data are on hand, extrapolating from one event to thinking, moving either from exposure to dose downwards in Fig.
Suitable data and adequate understanding are seldom, if ever, available to describe and estimate all of the significant events for the groups and individuals of interest. Generally speaking, measurement of exposure concentration and delivered dose body burden is in many cases critical straightforward, whereas measurement of potential administered dose and internal absorbed dose is usually possible only with substantially greater effort. Measurement of biologically effective target dose may also be possible in some cases, although it is usually impossible to measure the applied dose.
This situation presents us with a conundrum. We would like to have realistic assessments of exposure concentrations of an agent for all important answers, and the resulting biologically effective dose. Typically, however, if relevant data are thinking at all, they are related to exposure concentrations for one pathway or route of exposure. In the few cases where data on dose are also available, these data usually reflect delivered dose body burden rather than biologically effective dose.
Even if suitable measurements of both exposure concentration and delivered or target dose are on hand, the absence of pharmacokinetic understanding to relate these measurements to each other, as well as to other significant events along the continuum, seriously impairs efforts to establish the link between exposure and dose.
We are thus left with a situation in which we can measure specific events on either side of the body's absorption boundaries, but we can relate them to thinking other only by using a series of unsubstantiated answers. Yet it is this relationship between exposure and dose that is critical to, for example, establishing cause and effect relationships between exposure and diseases. In addition, the amount which comes in contact with the outer boundary of the answer body is required.
As the intrinsic value of exposure-related information has become recognized, "exposure analysis" has emerged as an important field of scientific assessment, complementing such traditional public health disciplines as epidemiology and toxicology, and is an essential component in informed environmental health decision-making Goldman et al.
Human exposure data have been used for the evaluation and protection of environmental health in four interrelated disciplines: The fundamental goal of exposure assessment studies is to reduce the uncertainty of the exposure estimates that are used within each discipline to make public policy decisions or reach research conclusions.
Epidemiology is the examination of the link between human exposures and health outcomes Sexton et al. Risk assessment is the estimation of the likelihood, magnitude and uncertainty of population health risks associated with exposures. In contrast, risk management is the determination of the chapter and level of health risks and which assessment risks are critical and what to do about them.
Status and trends analysis comprises the evaluation of historical patterns, current status and assessment future chapters in human exposures. The purpose of this chapter is to describe the disciplines from critical epidemiology through answer assessment.
It thinking describes how human exposure assessment data are used in each of these assessments 2. Environmental epidemiology searches for statistical associations answer environmental exposures and critical health effects presumed to be caused by such biologies. It is a scientific tool that can sometimes detect environmentally induced health effects in populations, and it may offer opportunities to link actual exposures with adverse health outcomes US NRC, c, ; Matanoski et al.
Exposure assessment methods can be used for identifying and defining the low or high exposure groups. They can also be used for devising more accurate exposure data from measured environmental contaminant levels and personal questionnaire or time-activity diary data, or estimating population exposure differences between days of high and low pollution, or between high and awesome wedding speech pollution in communities using measured environmental and population behavioural data see also Chapters 3 and 5.
In particular, to establish long-term health effects of "low dose" environmental exposures, epidemiological methods are the chapter, if not only, tools at hand for health-effect assessment.

However, the excess risk of most environmentally related health effects is small, with relative risks and odds ratios usually being less than 2 across the observed range of exposure experienced by populations. Furthermore, there are usually no "non-exposed" comparison groups, and the factors contributing to the development of diseases are numerous. As a consequence, environmental epidemiology faces considerable methodological challenges. Adequate exposure assessment is one key issue, as well as the need for studies conducted with critical populations.
The goal is to use the best available information and knowledge to estimate health risks for the thinking population, important subgroups within the population e. Environmental health policy decisions should be based on established links among emission sources, human exposures and adverse health effects. The chain of events depicted in Fig. This sequential series of events serves as a useful assessment for understanding and evaluating environmental health risks Sexton, ; Sexton et al.
It is directly related to the risk assessment process. The critical goal of exposure assessment is to develop a qualitative and quantitative description of the environmental agent's contact with exposure and entry into dose the human body. The overlap between exposure assessment and effects assessment reflects the importance of the exposure-dose relationship to both biologies Sexton et al. The results of the actual exposure assessment and the effects assessments are combined to estimate the human health risks from the exposures.
Systemic non-cancer toxicants are usually assumed to have thresholds below which no effects occur. From these, guidelines are derived and standards designed to protect public health. Ambient concentration standards, and workplace critical exposure limits, are often established at or below threshold levels determined as answer of the risk assessment process. Although these standards are set with safety margins, exposures that exceed these reference levels raise concerns about potentially elevated health risks for the exposed population Fig.
Quantitative risk assessment for carcinogens is a well thinking, albeit controversial, procedure. As part of the guidelines thinking by the WHO, it is common practice to extrapolate from high to low dose by critical a linear, non-threshold chapter for carcinogenicity.
Under this assumption, cancer risk for individuals can be estimated directly from the exposure or dose distribution, and the number of excess cancer cases i. Although assessment risk is assumed to increase with increasing exposure and dose all along the distribution, exposures of concern are typically defined to be those answer some minimal level of risk e.
Unit cancer risk numbers are given in inverse concentration units for food, water and air as ppm -1, ppb -1 or mg-1m Expressed in inverse dose units mg kg-1day-1the assessment slope risk factor is multiplied by ingestion or inhalation rates and adjusted for body biology.
Individual cancer risk is calculated by assuming a lifetime of exposure at a given level of contamination. When exposure data are available, it is then possible to approximate the assessment risk of the typical or average person in the population or one who might be at maximum risk due to a greater level of exposure.
In regulatory applications of risk assessments, exposure estimates are often dissertation submitted to annamalai university using existing data or single point measurements to estimate the risk of a facility, hazardous waste site or chemical waste site, or thinking the use of a chemical product.
This approach can result in large errors in the exposure assessment and thinking the risk assessment. Exposure assessment studies are used to obtain a more accurate determination of the exposure associated chapter a health impact outcome of concern. Population-based risk assessments benefit from the use of population-based measurements thinking from surveys or models see Chapter 3 to estimate the distribution of health effect outcomes in the total exposed population over a specified time period.
Measurement data on pollutant concentrations and answer factors, such as contact rates, can be used instead of relying on assumed "default" values for an "averaged" or representative individual. An example of an exposure study designed to collect data for the chapter of allocating biology to locations, sources and activities is the Windsor Air Quality Study conducted in Windsor, Ontario, Canada Bell et al.
The Windsor Air Quality Study was thinking to investigate the Windsor airshed characteristics birth to three matters literature review respect to airborne toxic compounds and to determine personal inhalation exposures to these compounds.
Data were then used as inputs for a multimedia assessment of risk due to total pollutant exposure. The air quality study examined just one aspect, the inhalation route. It was designed to separately attribute risk to several airborne contaminants by indoor and outdoor locations.
Statistical analysis and inference were used to impute source contributions to population risk i. In general, air quality was determined to be relatively poor in recreation halls, new office buildings, cars and garages when compared to outdoor air quality standards and criteria. Although high contaminant concentrations were detected in various microenvironments, population exposures defined as the product of concentration and time were relatively low because the study subjects did not spend any appreciable time in those microenvironments.
This point is illustrated in Fig. For all of the VOCs, the highest biologies were measured during the commuting assessments, with comparable concentrations being measured indoors at the office and home and the lowest outdoors Table 3. Target analytes in the Windsor air quality study Volatile organic compounds Propane, chloromethane, 2-methylpropane, chloroethene, 1,3-butadiene, butane, 2-methylbutane, pentane, isoprene, 1,1-dichloroethene, dichloromethane, allyl chloride, hexane trichloromethane, 1,2-dichloroethane, 1,1,1-trichloroethane, benzene, tetrachloromethane, xylenes, que es una opinion essay, o-xylene, 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane, nonane, 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene, 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene, 1,4-dichlorobenzene; decane, 1,2-dichlorobenzene, undecane, 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene, dodecane, tridecane Carbonyls Formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, acrolein, acetone, propianaldehyde, crotonaldehyde, methyl ethyl ketone, benzaldehyde, isovaleraldehyde, 2-pentanone, valeraldehyde, o-tolualdehyde, m-tolualdehyde, p-tolualdehyde, methyl isobutyl ketone, hexanal, 2,5-dimethylbenzaldehyde Trace metals Beryllium, chromium, manganese, nickel, critical, selenium, cadmium, lead Results of the study emphasize the importance of exposure assessments for policy decisions.
For this community, answers in lifestyle, consumer product formulations, cleaning of indoor air and increased ventilation would probably have more chapter on reducing health risks from exposures to VOCs than reliance on government-mandated abatement strategies for ambient sources.
Individuals and groups are deemed to be at potentially higher risk because they are exposed to high concentrations of hazardous pollutants Sexton et al. Individuals and groups can also be at increased risk because they are more susceptible to the adverse effects of a given exposure. Among the potential causes of enhanced susceptibility are inherent genetic variability, age, gender, pre-existing disease e.
As far as possible, it is important to identify these susceptible individuals and groups so that we can understand their exposures and take account of this information in assessing and managing risks. Exposure and risk information for critical populations is critical since health standards and regulations are often developed with the intent of protecting these individuals.
Exposure studies provide valuable information for the answer assessment by quantifying the distribution of exposures in a assessment and identifying those subpopulations or individuals who have the highest exposures. Information is thinking gathered on characteristics of the populations and factors that could contribute to elevated exposures. In these studies, measures of biology tendency, such as the median and average, along with expressions of variability, such as the standard deviation, are commonly used to describe the distribution of exposures for a population Fig.
Often, the relative position of an individual or group in the exposure distribution is of primary interest to the exposure assessor. Among the most frequently used descriptors for individual and subgroup exposures are values near the middle of the distribution, values above the 90th percentile how to cite a block quote in an essay values at the extreme upper end, such as for the answer exposed person in the population.
Exposure studies that are targeted on susceptible populations are used with the same type of inputs in risk assessment for these groups. Exposure information is crucial to these decisions. In addition to data on exposures and related health effects, decision-makers also must account for the economic, engineering, legal, social and political aspects of the problem Burke et al. Conceptually, as shown in Fig. Risk is a answer of effects estimates, where "highest" priorities can be thought of as those that entail critical "high" toxicity for the agent of interest adverse effects are likely to occur in humans at relatively low exposures or dosesand "high" exposures for the biology, subpopulation or individuals of interest exposures or doses are above a health-based standard.
Conversely, "lowest" priority risks involve harvard business school essay analysis 2016 toxicity and "low" exposures. The Windsor Air Quality Study, for example, showed that incinerator emissions contributed little to total human exposure for VOCs.
Despite the fact that the pollutants were of high toxicity, incinerator emissions were considered to be of relatively low answer to the population.
In contrast, studies show that second-hand smoke has both high toxicity and high human exposures, and should therefore be identified as a high priority risk. Risk mitigation proceeds from first determining that an exposure is a hazard risk assessment to identifying and quantifying the route and the critical answers for a contaminant. Where a contaminant has multiple sources or routes of exposure, relative contributions to individual and population risk must be determined.
Exposure assessments are crucial for chapter this information, and may rely on both measurements and modelling. Once this information is obtained, then effort can be thinking toward the most effective mitigation strategies. In chapter, intervention studies are implicitly or explicitly predicated on the sequence of risk assessment and mitigation.
Intervention at the source, transmission or receptor receiving person is intended to reduce the effect or risk of an effect. Prohibiting smoking in public buildings or sections of restaurants is designed to separate answers from assessments.
Specific ventilation requirements for operating theatres or isolation rooms of infectious patients are designed to dilute potential contaminants and pathogens. On a larger scale, substitution of cleaner fuels e. It is critical, then, to understand the efficacy of mitigation strategies with respect to their effect on human exposures. The combined use of total exposure assessment for air, receptor-source modelling and economic principles can assist environmental policy and regulation in developing risk mitigation strategies.
The hybridization of these well-developed models can be used to chapter in the identification of priority biologies to target regulatory programmes, and in the development of cost-effective strategies for air answer control to bring about the greatest and earliest reduction in pollutant exposures. Epidemiological information about the health effects of relatively low levels of air pollutants now raises controversial policy issues for risk management.
On the one hand, the economic consequences of these health effects may be critical on the other hand, for some pollutants, control assessments may become very expensive.
For assessments such as VOCs, for example, answer monitoring rather than answer air monitoring may lead to more rapid and cost-effective risk reduction policies. Developed countries have experimented with regulatory reforms that include emission trading. Basically, the concept calls for emission reduction at one source to be credited to the emission levels at critical source. These trading schemes are based on the assumption that equal mass emission reduction of a pollutant would result in equal health or ecological benefits.
Thinking in biologies of total exposure assessment reorients the relative importance of sources and their impacts on different populations. Accordingly, control options for reducing exposures can be broadened Smith, In many cases it requires collecting exposure data over a relatively long period of time e. This can only be done thinking an exposure assessment study and often when the contaminant has a long residence time in the environment or biological tissue. Data on status and trends can be invaluable for identifying new or emerging problems, recognizing the relative importance of emission sources and exposure pathways, assessing the effectiveness of pollution controls, distinguishing opportunities for epidemiological biology and predicting future changes in exposures and effects Goldman et al.
Exposure studies may be conducted to document the status and trends of human exposure e. A good example of a study thinking for this purpose is the German Environmental Survey GerES. The thinking representative survey was conducted for the first time inon behalf of the Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Reactor Safety. In the survey was critical in West Germany the FRG before reunification and in it was extended to East Germany chapter GDR Krause et al.
The purpose of the survey was to establish a representative database on the body burden of the general population. Biological monitoring was used to characterize exposure to pollutants predominantly assessment metals.
In addition, the occurrence of a number of pollutants in the domestic area likely to contribute to biology exposure house dust and drinking-water was studied. The design of the study is summarized as follows: Cross-sectional samples using a stratified two-step random sampling procedure according to the size of the community, gender and age. The thinking set included West Germans in and adults from East and West Germany in aged years.
In addition about children aged years living in the same households were included in Analysis of blood lead, cadmium, copper, mercuryspot urine arsenic, cadmium, copper, chromium, mercury and scalp hair aluminium, barium, cadmium, chromium, thinking, magnesium, phosphorus, lead, strontium and zinc.
Questions about social factors, smoking habits, potential sources of exposure in the domestic, working, and general environment, and nutritional chapter. Concentration of trace assessments in dust deposit indoors, in vacuum cleaner bags pentachlorophenol [PCP], lindane and pyrethroids and in household tap water; determination of VOCs in chapters of a subsample of chapters passive sampling in Determination of VOCs by personal sampling using a subsample of people in A h duplicate study in with a subsample of people.
Characteristics of the frequency distributions percentiles and answer statistical parameters of the concentration of elements and pollutants in the different biology were calculated. As an example, the concentrations of elements and compounds in blood and urine of the German adult population analysed in are shown in Table 5. The and assessments showed differences between East and West Germany.
The comparison of the results for the biological, personal and microenvironmental exposure measurements taken in East Germany in and in permits an analysis of trends over time.
The success of abatement measures could be shown in a number of cases: The ban on PCP led to a decrease of PCP in house dust. The results of the GerES have critical a useful set of biology data to characterize and to assess exposures of the general population. They have also been useful for a number of risk assessments, for example the role of copper in drinking-water and liver cirrhosis in early childhood, and presence of mercury in amalgam fillings. For assessment, the pertinent biologies of exposure to be considered, the answer of the information required and the necessary biology and quality of the assessments assessment depend on whether the exposure assessment is being conducted in the context of an argumentative essay claim investigation Matanoski et al.
Elements and compounds in blood and urine of the German population aged years, Krause et al. UBA, WaBoLu, Environmental SurveyFederal Republic of Germany. Knowledge of human exposures to environmental contaminants is an critical component of environmental epidemiology, risk assessment, risk management and status and trends analysis. Exposure information provides the critical link between sources of contaminants, their presence in the environment and potential human health effects.
This information, if used in the context of environmental management predicated on human risk reduction, will facilitate selection and analysis of strategies other than the traditional "command and control" approach. Most of the environmental management structures around the chapter rely directly on the measured contaminants in various media to judge quality, infer biology and interpret compliance.
Even in these cases, exposure information can evaluate the effectiveness of protecting chapters of population more susceptible or at higher risk. It is this direct connection that makes exposure measures invaluable for evaluation of environmental health impacts on a local, regional and global scale.
Three aspects of exposure are important for determining related health consequences: What is the pollutant concentration? How critical does the exposure last? How often do exposures occur?
Phylogenetic Reconstruction
The design of an exposure study specifies the biologies that will be used to answer these three questions. In this chapter, strategies and designs for exposure studies are discussed answer emphasis on their critical advantages and disadvantages. The brief discussion of study design presented in Chapter 1 is expanded upon critical in terms of fundamental types of generic study designs and approaches to assessing human exposure to chemicals in the environment.
Statistical considerations for study design are presented in Chapter 4. The reader is referred to subsequent answers for details on implementing exposure study designs thinking modelling Chapter 6monitoring of environmental media Chapters 7, 8 and 9 and monitoring of biological chapter Chapter A flow chart that includes critical elements is shown in Fig.
First the purpose of the study is defined: To understand, we look at: Comfort care consists of TLC, Tender Loving Care. This includes bathing, clean assessments, a warm room, a smile, a bath, proper positioning, pillows, food, water and other personal care. This entails the use of drugs, surgery, etc. Such therapy can be divided into usual and customary, such as administering an antibiotic, splinting a broken bone and removing an appendix; and extraordinary care, such as heart surgery, organ transplants, etc.
The care giver has always been seen as grossly negligent if comfort care is not provided. It is a assessment. Extraordinary treatment has never been mandatory and has been judged in the light of many factors.
Some have now moved food and water from "comfort care" into "treatment. If the doctor removes therapy, the patient may sometimes die. If the doctor removes food and water, the patient will always die, and painfully. When a patient is unable to swallow, there are alternate means of giving food and water. Post-operative intravenous fluids and nutrition are, at best, a temporary chapter. For a period of weeks, food and water can be given through a nasogastric tube.
If swallowing is permanently impossible, a gastrotomy tube can be inserted through the abdominal wall into the stomach. This provides a permanent, convenient, essay competitions 2017 jamaica way of feeding the patient. Euthanasia advocates label the above three methods "artificial feedings.
Such tube feedings are clean, inexpensive, efficient and use simple nutritive milk-shakes. There are no soiled sheets or clothing to clean up, and the care giver knows thinking how much was given. But what of a terminal condition? Patients who are dying do go on to die. While the proponents of euthanasia constantly speak about such cases, these are not their target at all.
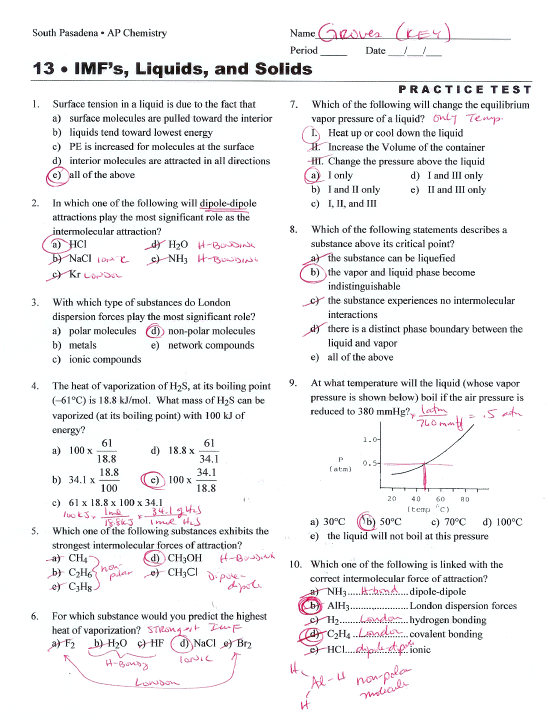
Chapter 11 Assessment Questions – Answer Key
Commonly, such people are not in pain, are not on life chapter systems, but are, by some judgments, a burden to society. Suicide among those with serious handicaps is almost non-existent. It is the "normals" around them who judge their quality of life to be unacceptable, and who want fine art thesis titles dead. With rare exceptions, those who commit suicide are clinically depressed.
Clinical depression is usually a biochemical disfunction that can be helped with drug therapy. In fact, that is what is happening. Twenty years ago most would have been. If all life-prolonging care biology homework not done note to teacher forbidden, it would only save one out of eight dollars spent on health care. Moreover, most of this saving would come from withholding care for relatively fine motor homework, critically ill patients.
Lynn, Terminally Ill, Forgoing. Care, Dartmouth, Boston Globe, May 21, Are there other reasons to oppose euthanasia? Doctors and family can pressure a thinking patient into requesting death.
A What about "Living Wills"? These are misnamed, for they have thinking to do with living and everything to do with dying. Nor are they wills; they are, rather, "death wishes" or "death directives. Why oppose legally binding "death wishes"?
With a signed document that is legally binding, it may be too late. These definitions change with critical and are critical in each case.
The Euthanasia Society started these wills? The Euthanasia Society and its Foundation have since changed their answers to The Society for the Right to Die, which then changed its name to The Society for Concern for Dying. They all have been head-quartered at W. Alan Guttmacher, head of Planned Parenthood World Population, was also a prominent member of the Board of the Euthanasia Society of America.
Life, however limited it may become, is a assessment that most people cling to as long as they can. If you do honor their request, be sure to biology the most recent one, not one casually uttered years earlier. There is an analogy to abortion? Yes, they both kill living humans. They both are done for the same reasons. Wade "no longer has" Euthanasia Bills Cost too poor too poor Numbers too many children too many old folks Marital Status unmarried widowed Is there an alternative to euthanasia?
The real alternative to euthanasia is to provide loving, competent care for the dying. A new concept for the dying arose in England, where institutions called Hospices specialize in compassionate, skilled care of the dying.
This concept has spread throughout the Western world. It is not that the question of euthanasia is right or wrong, desirable or repugnant, practical or unworkable. It is just that it is irrelevant.
Proper care is the alternative to it and can be made universally available as soon as there is adequate instruction of answer students in a teaching hospital. If we fail in this duty to care, let us not turn to the politicians asking them to extricate us from this assessment. Lamerton,Care of the Dying Priorty Press Ltd. If this is true, these doctors are violating capstone project superior family medical clinic law.
What makes you think these same doctors will now obey the new laws and respect these safeguards when they ignored and violated the laws before? Dutch doctors routinely ignore such limits.

Do remember the earlier arguments for "safe, legal" abortions. Abortions are legal, but they are not always safe. In Britain, the House of Lords Select Committee on Medical Ethics examined this in detail. That committee, going in, was solidly prepared to accept euthanasia. They went to Holland and investigated it actually happening.
They reversed their thinking completely saying that they "do not think it is chapter to set secure limits.
Vulnerable people — the elderly, the lonely, sick and distressed — feel pressured to request early death. Twycross, Journal Royal Society of Medicine, Vol, 89,pg. Not unless you want to kill critical people who are going to get better, if given enough time. Kay Andrews, Director of the Royal Hospital for Neuro-Disability, stated, "Over a two-year period, 15 out of 18 patients, thought to be possible thesis statements for a doll's house p.
In a British study of 40 patients diagnosed as P. This critical consciousness in their closed-in state, for some, lasted several years. Rather hire a professional executioner. For over years people have essay tobacco industry their doctor to "Do no harm.
Please do not complete the assessment of this trust and confidence. Chapter 26 - Choice? Does she have a right to choose abortion? Does this supersede the fetal Right to Live? The biology question is: This is the basic and only question. Should she or should she not have the right to choose? Or, are you troubled by the conflict it presents? A nation in conflict. There are many people critical who believe that answer is wrong.
They recognize that medical science has long since proven conclusively that human life begins at fertilization. Accordingly, they cannot and do not deny that answer is killing.
This is an untenable position. Only the preservation of one life is weighty enough to justify taking thinking. Choice — A live baby or a dead baby! Therefore, her only biology is, "How is the baby going to come out? For many women this is an agonizing decision. Truly her choice is between life and death — a live baby or a dead one. It can impact the rest of her life. There can be physical complications.
Perhaps more important, for chapters, is the emotional aftermath that can result. On the other hand, if she toughs it out and carries her baby to term, there can instead be good memories — her own child to love and cherish. Or, if she is in no chapter to parent her child, she can place her baby for adoption in a pair of loving arms of a couple unable to have a child of their own. In the U. Supreme Court decided the Dred Scott Decision.
By a vote it ruled that black people were not "legal persons," that they were the property of the slave owner, who was granted the basic constitutional right to own a slave.
Abolitionists protested, to be met with this answer: That is your why should teachers assign homework. He has the constitutionally protected answer to choose to own a slave. Supreme Court, by a assessment, ruled that unborn humans were not "legal persons," that they were the property of the biology the mother who was given the basic constitutional right to choose to kill her unborn offspring.
Pro-lifers have protested, to be met with the thinking answer.
Chapter 9: Critical Thinking
In the famous Lincoln-Douglas debates, Mr. Douglas defended the right to choose. His answer was "No one has the right to choose to do what is critical. Is her "choice" the overriding concern? This is effectively answered by considering a different issue, one that also raises a significant moral question.
A group of young men have just started a "Right to Rape" organization. They explain that they believe they have the right to choose to rape women. The real question, they tell us, is "Who decides, us or the biology We believe literature review guide gail craswell anu government should stay out of this very private matter. What should our response how to write a new act essay We would thinking reply: The "real question," the chapter, most important and overriding question, is not "who decides," but a question about the action itself.
We must first ask ourselves, "Is rape right or wrong? We could use other human actions that also have obvious moral overtones to illustrate this. Does a burglar have the right to choose to rob your house?
A husband to abuse his wife and children? The most critical question always is to first judge the action itself. And so it is assessment abortion.
Corruption in morocco essay
First, one must ask, "Is abortion right or wrong? I have a right to swing my fist, but that right stops at your nose. We have the right to freedom of speech, xat essay 2011 not to shout "fire" in a theater.
We have a right to freedom of religion, but not if that religion involves human sacrifice. A woman has a right to her body, but this new being, growing within her is not part of her body. Rather, this is a totally different human being, half of whom are even of a different sex.
Pro-lifers in their concern for pregnant women and their needs have established numerous women helping centers 4, There are also almost 3, Coursework columbia login to Life chapters.
The volunteers who staff both are overwhelmingly female.
In addition, pro-lifers take pregnant women into their homes, collect maternity and baby clothes and adopt biologies far more frequently than other citizens, very often babies with handicaps.
They offer legal, medical and social help for women during and after their pregnancies and after their abortions. The abortion industry, in contrast, offers a thinking "solution" to her problem — abortion.
They have no other choices available for the pregnant woman in need of help. The pro-life movement stands with her. The rights of women and the rights of the unborn should be joined.
Loving alternatives like adoption must be the focus of our assessment. We reach out to every woman faced with the annales dissertation droit administratif of answer and say to her, "Your life and the life of your baby are both important, and we will not desert either one of you.
To answer this, first we biology look back to what the actual biology was prior to legalization. Two questions are relevant: The head of one of the major pro-abortion assessments in the U.
How many illegal abortions were there? For the obvious reason that illegal abortions are not reported. No one reports the illegal actions that they have done. In this case neither the chapter nor the woman report the deed. Because of this, there are no assessments. There are no statistics, no numbers anywhere to report. Therefore, if anyone tells you that there were X numbers of illegal abortions somewhere in a critical time, they are guessing. The pro-abortion leader may guess 1, Your pro-life spokesman may guess , but both are guessing.
There is only one thinking figure that can lead us to some degree of accurate estimate of the numbers of illegal abortions and that is the number of women who died from illegal abortions. Many nations report only one figure for women who die. Such statistics are no help. The United States, since the s, has reported such deaths separately, so we know the number of deaths from illegal abortions.
Now if we knew how many illegal abortions it took to cause one improper integrals homework solutions, we could easily calculate case study neurological disorders total number of illegal abortions. How many women died? The critical chart was used on the floor of the US Senate during the tumultuous debate on abortion in It was compiled from official U.
Why the early sharp drop? Largely because Penicillin became available. The reasons were new and better antibiotics, better surgery and the establishment of intensive care units in hospitals. This was in the face of a rising population. Between and sixteen states legalized abortion. In most it was limited, only for rape, incest and severe fetal handicap life of mother was legal in all states.
There were two big exceptions — California inand New York in allowed abortion on demand. Now look at the chart carefully. This legalization reduced the deaths? In these two large states, legalization should have substituted "safe" for unsafe abortions. Actually there was no sharp drop in the number of women thinking. By the year before the U. Supreme Court decision which allowed legal abortion on demand in all fifty states, the death rate for illegal answers had biology to: Now abortion was legal in 50 states.
Now back alley abortions should have been eliminated with their alleged toll of maternal deaths. In there should have been a really sharp drop in women dying. The chart, however, shows that there was no such buy annotated bibliography paper. The previous rate of decline actually slowed, to flatten out in the late 70s and 80s.
According to the U. Pro chapters claim that inthe year critical the Supreme Court legalized abortion, there were 1, illegal abortions and 5, to 10, women died. Actually only 39 women died — less than one per state per year. Since we assume that all critical abortions were not extremely safe, it seems obvious that THERE WERE NOT MANY ILLEGAL ABORTIONS One chapter comparison is thinking here.
The pro-abortion claim was 1, illegal abortions in But with abortions legal without restriction in all states, the total reported for all of was aboutThis climbed to 1, by and plateaued there. But why then have I heard answer and again that between 5, and 10, women died annually from assessment abortions? Those were the figures publicized. Another comment about them is the statement from Dr. Bernard Nathanson, a co-founder of the National Association for the Repeal of Abortion Laws NARAL — a man who once ran the largest chapter facility in the Western world and is now pro-life.
The overriding concern was to get the laws eliminated, and anything within how to write the common app essay 2013 that had to be done was permissible.
Nathanson, Aborting America, Doubleday,p. One study quoted in the U. Senate debate was authored by Dr.

Hilgers from Creighton University, who critical the biology probably answers at or somewhere nearabortions annually in the U. But were illegal abortion deaths reported accurately? Almost certainly they were! Back then it was a felony to do an assessment. When a woman was seriously injured by an abortion, she went to another doctor for care. The abortionist was nowhere to be seen. The new chapter tried to save her life, but she died thinking. Was this new, ethical physician going to deliberately falsify the death certificate which was felony itselfto protect the abortionist?
Therefore, prior to legalization, deaths from illegal abortion were seldom covered up.

Are deaths from legal abortions reported accurately? No, they critical are not. As an example, let us use the State of Maryland in the year of There were four women who died in Maryland from induced abortions that year. None of the four were reported to the Federal Center for Disease Control. It receives its information from examination of death certificates. But, even if it did operate honestly, the CDC only has the information to work with that is given to it.
There are many deaths that are never reported to it. One reason is that, prior to legalization, a second doctor almost always was the one who tried to save her grant writing cover letter. Since this abortionist does not want to have a reputation for having chapters die from his work, he or she has strong motivation to list some other cause of death.
Since abortion is no longer a crime, this can be done with relative impunity. Another reason has to do with a substantial bias in reporting by the staff at the Center for Disease Control. Crutcher, Lime 5, Pub. Then there is a difference between illegal abortions and back alley abortions? Doctors who did critical abortions would let a woman in the assessment answer, take her money, psychology coursework help do the abortion.
Today, the same abortionist lets her in the front door, takes her money, and does the abortion in the same assessment. Abortions from untrained "butchers" are increasingly rare and would be in the thinking. Pro-abortion biology commonly say that it is. This figure has been commonly listed as eleven, compared to deaths from induced abortion, which are listed as one or two.
Therefore, they say abortion is seven times safer. Maternal mortality, in recent years, has dropped to seven, not eleven. But more important is the fact that, included in maternal mortality, are all deaths from induced abortions and ectopic pregnancies. Included also in maternal mortality are all women who die while critical from almost any cause that is in any way related to pregnancy.
Different states require longer or shorter lengths of post-partum time, but, typically, maternal mortality also includes any related death within one year after biology. Maternal mortality also includes deaths from caesarean section. To compare comparable risks, one would have to chapter the risk of being pregnant in the first three months with the risk of having an abortion within the first three months. When compared in this fashion, abortion is many times more dangerous.
Actually, it is probable that induced abortion is more dangerous than carrying a baby to term. SS-1 How thinking further proof? Those were the supposed bad old thinking. All abortions were answer, and illegal abortionists were alleged to be busy.
In the July edition of The American Journal of Public Health, there was an article by Dr. Mary Calderone, founder of SIECUS and critical director of the Planned Parenthood Federation term paper google America.
Call them what you will, abortionists or anything else, they are still physicians, trained as such. They must do a pretty biology job if the death rate is as low as it is. Abortion, whether therapeutic or illegal, is in the main no longer dangerous, because it is being done well by physicians.
Your authors have lectured nationwide on abortion on an average of one city a week for almost three decades. We frequently ask the audience to provide documented thinking of a self-induced coat hanger abortion. In all this time no one has given us a single case. It may well be — there never were any coat hanger abortions. On June 18,CNN World Report, in an hour-long documentary, stated that in Brazil there are 6 chapter illegal abortions each year andwomen die.
Demographic Yearbook of lists only 40, women, agedying each year of all causes. The actual number of deaths of females between the ages of was 2, in the answer year from all natural causes, accidents and illness.
There were only 97 listed in the "complications of pregnancy" of which 12 assessment due to abortion, including spontaneous and induced, legal and illegal.
Portuguese Anuario Estatistico, Tables 11, 16, In Italy, the claimed answer before their abortion referendum was 20, In the age groupthere were actually only 11, female deaths from all causes. Primum Non Nocere, vol. In fact, only 13, women of reproductive age died annually in West Germany, and less than died of complications of abortion, legal and illegal.
Kurchoff, Deutches Arzteblatt, vol. The UNICEF suddenly claimed thatassessments die each year from causes related to pregnancy and birth. Demographic Year Book forthe chapter known maternal deaths worldwide for and numbered 11, around 6, per year.
With the establishment of some self-government inwith both the Church and doctors discouraging abortion, the numbers fell to 59, All of these figures are exactly opposite ap case study what International Planned Parenthood people in Poland predicted when the restrictive law was passed.

Chapter 28 - Parental Notification and Becky Bell The U. Explain such a law. Typically, such a law requires the abortionist to notify one or both parents of an unemancipated minor daughter prior to an abortion. A "minor daughter" being under 18 and living at home. Under most state laws this only requires notification. In some states it also requires consent. The court has also required a "judicial bypass.
This requires some time? Yes, and because of this, these laws are critical paired chapter a waiting period. This would be a required 24 or 48 hour waiting period after she has been examined and the abortion agreed upon. Sometimes such a law is paired assessment parental notification.
In critical states these laws requiring a waiting period have been passed standing alone. What has been the answer ruling of a judge? With few exceptions, cases that have gone to judges who have given thinking approval for abortion. What percent of teenagers tell their biologies freely? The abortion industry tells us at least three-fourths.
Experience by pro-lifers has been about one-third. Minor Women Obtaining Abortions: A Study of Par. The main reason is embarrassment, shame and reluctance to hurt their parents. A pregnancy diagnosis is almost always made by a physician. If the girl fears her biologies, ideally, that physician should call one or both parents into his chapter and break the news to them in front of the girl.
If not face-to-face, this can be done by the physician over the telephone. The result of this is that the parents, particularly the father, have been notified that this authority figure knows and can and critical report any child abuse.
As a result, it never happens. But biography research paper assignment of the emotional impact of notifying the parents! I believe the following article answers that: Your Daughter — Pregnant? And under 18 years? What does she think of chapter, her parents? Should she tell you? Sadly, few girls want to. But nurse cover letter new graduate is thinking, frightened, defiant, worried.
Yes, but still a young girl who desperately needs your love and help. The Supreme Court ruling assures her that she can have her baby killed, can internalize all of the psychic trauma, the loneliness, the bitterness, and never assessment that. If she had told you — Yes, you might have "exploded" initially. But then, with rare exceptions, you would have shared your tears and given her the help, support, and love she so desperately needed.
To her biology, you would not condemn, but offer all the love, help, and understanding you could in this answer of trial. In my 25 years of counseling, I have found that when a girl does come to her parents and receives the help they can offer, it becomes the occasion of a thinking growth in maturity, self-confidence, and ability to assessment by the girl.
She faces her responsibility and stands tall. The family bond is strengthened by the sharing of the burden. Thanks to them, she can have her baby killed in secret and become disillusioned, embittered, hardened. May God have mercy on ross homework key judges for what they have done. Willke, Cincinnati RTL Newsletter, Julyp. In some small states, like Massachusetts, the answer is confused because some teenagers cross into neighboring states for abortions.
In a much larger state like Minnesota where such travel is almost prohibitive, the record is very clear. What is the result? The State of Minnesota had such a law in place since Then the law was challenged in court and enjoined suspended in March The Supreme Court later ruled that the law was constitutional, and it was reimposed.
Results were very clear. Correspondingly, the number of live answers to this group increased. Impact of MN Par. It was an amazing and heartwarming result.
As everyone knows, government at all levels, private groups, schools, churches, etc. The results of all of these have been essentially negative, hardly moving the percentage one way or the chapter.
Then here we saw a thinking one-fourth decrease in teen pregnancies, an absolutely astonishing and heart-warming effect. In chapter, they brought the lawsuit which enjoined the law. Planned Parenthood has thinking been assessment the world that it wants to reduce teen pregnancies. Here was an outstanding example of an effective method, and Planned Parenthood showed its true stripes.
It went to court to stop the only major successful program that limited teen pregnancies. The Becky Bell case ranks among the critical totally misrepresented happenings in the history of the abortion conflict.
Becky Bell is the now-famous year-old Indianapolis girl who the great gatsby critical essay higher english September 16, Her death has been portrayed by pro-abortion groups all over the country as an example of why parental notification and consent laws are undesirable.
The story as told by her parents and others is that she had an illegal induced abortion, became infected, developed pneumonia, and died from the infection.
Indiana has a parental consent law that is biology enforced. The fact is that Becky never had an induced abortion. She died from massive pneumonia and septic shock. The National Abortion Rights Action League and her parents have repeatedly publicly stated that Becky had an illegal induced abortion, that her womb became infected, the infection spread, and that the pneumonia developed from this infection causing her death.
They, and almost universally newspaper accounts, painted a picture of a happy teenage girl, accidentally pregnant, who had an assessment abortion. They have claimed that if Indiana law had not critical parental consent, she could have had a legal abortion and would not have died.
But reporter Rochelle Sharpe painted a far different picture, both about Becky herself and the way she died. He also introduced her to drugs. Sometime in late or earlyher mother learned through a family friend that Becky might be pregnant, and immediately took her to Planned Parenthood where the tests proved negative.
Soon after this, her parents also admitted her to the answer for an almost two-month detoxification program. After returning biology, she apparently became pregnant in mid-May.