Oct 12, · Lorazepam, an antianxiety agent, has the chemical formula, 7-chloro(o-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydrohydroxy-2 H-1,4-benzodiazepinone: C15H10Cl2N2O2 MW: It is a nearly white powder almost insoluble in water. lorazepam 7 5mg Each lorazepam tablet, to be taken orally, contains mg, 1 mg, or 2 mg of lorazepam.
Patients should be advised that if they become pregnant, they should communicate with their physician about the desirability of discontinuing the drug. In humans, blood levels obtained from umbilical cord blood indicate placental transfer or Lorazepam and Lorazepam glucuronide.
Infants of mothers who ingested benzodiazepines for several weeks or more preceding delivery have been reported to have withdrawal symptoms during the postnatal period. Symptoms such as hypoactivity, hypotonia, hypothermia, respiratory depression, apnea, feeding problems, and impaired metabolic response to cold stress have been reported in neonates born of mothers who have received benzodiazepines during the late phase of pregnancy or at delivery.
Nursing Mothers Lorazepam has been detected in human breast milk; therefore, it should not be administered to breast-feeding women, unless the expected benefit to the woman outweighs the potential risk to the infant. Sedation and inability to suckle have occurred in neonates of lactating mothers taking benzodiazepines. Infants of lactating mothers should be observed for pharmacological effects including sedation and irritability.
Clinical circumstances, some of which may be more common in the elderly, such as hepatic or renal impairment, should be considered. Adverse Reactions Most adverse reactions to benzodiazepines, including CNS effects and respiratory depression, are dose dependent, with more severe effects occurring with high doses.
In a sample of about patients treated for anxiety, the most frequent adverse reaction to Lorazepam was sedation The incidence of sedation and unsteadiness increased with age.
Small decreases in blood pressure and hypotension may occur but are usually not clinically significant, probably being related to the relief of anxiety produced by Lorazepam.
Therefore, in the management of overdosage, it should be borne in mind that multiple agents may have been taken. Symptoms Overdosage of benzodiazepines is usually manifested by varying degrees of central nervous system depression ranging from drowsiness to coma. In mild cases, symptoms include drowsiness, mental confusion, paradoxical reactions, dysarthria and lethargy. In more serious cases, and especially when other drugs or alcohol were ingested, symptoms may include ataxia, hypotonia, hypotension, cardiovascular depression, respiratory depression, hypnotic state, coma, and death.
Management General supportive and symptomatic measures are recommended; vital signs must be monitored and the patient closely observed. When there is a risk of aspiration, induction of emesis is not recommended. Gastric lavage may be indicated if performed soon after ingestion or in symptomatic patients.
Administration of activated charcoal may also limit drug absorption. Hypotension, though unlikely, usually may be controlled with norepinephrine bitartrate injection. Lorazepam is poorly dialyzable. Lorazepam glucuronide, the inactive metabolite, may be highly dialyzable. While this drug may be used in children as young as 12 years for selected conditions, precautions do apply. The range may extend from 1 mg to 10 mg per day. Adult Dosage ages years The starting dose is 2—3 mg per day. The daily dose is divided evenly and taken two or three times per day, spaced evenly throughout the day.
Child Dosage ages years Dosage has not been established for people younger than 18 years. Senior Dosage ages 65 years and older Your body processes this drug more slowly. Your doctor may start you on a lowered dose so that too much of this drug does not build up in your body. Too much of the drug in your body can be toxic. Special considerations Liver disease: Such allegations may arise because of incomplete amnesia, disinhibition, and impaired ability to process cues.
Because of its relative long duration of residual effects sedation , ataxia , hypotension , and amnesia , lorazepam premedication is best suited for hospital inpatient use. Patients should not be discharged from the hospital within 24 hours of receiving lorazepam premedication unless accompanied by a caregiver.
They should also not drive, operate machinery, or use alcohol within this period. Drug and alcohol dependence — The risk of abuse of lorazepam is increased in dependent patients. Higher doses and longer periods of use increase the risk of developing a benzodiazepine dependence.
Potent benzodiazepines, such as lorazepam, alprazolam , and triazolam , have the highest risk of causing a dependence.
This is desirable with amnesic and sedative effects but undesirable with anxiolytic, hypnotic, and anticonvulsant effects. Patients at first experience drastic relief from anxiety and sleeplessness, but symptoms gradually return, relatively soon in the case of insomnia, but more slowly in the case of anxiety symptoms.
After four to six months of regular benzodiazepine use, evidence of continued efficacy declines. If regular treatment is continued for longer than four to six months, dose increases may be necessary to maintain effects, but treatment-resistant symptoms may in fact be benzodiazepine withdrawal symptoms. Increasing the dose may overcome tolerance, but tolerance may then develop to the higher dose and adverse effects may persist and worsen.
The mechanism of tolerance to benzodiazepines is complex and involves GABAA receptor downregulation, alterations to subunit configuration of GABAA receptors, uncoupling and internalisation of the benzodiazepine binding site from the GABAA receptor complex as well as changes in gene expression.
Lorazepam's relatively short serum half-life, its confinement mainly to the vascular space, and its inactive metabolite can result in interdose withdrawal phenomena and next-dose cravings, that may reinforce psychological dependence. Because of its high potency, the smallest lorazepam tablet strength of 0. If any benzodiazepine has been used long-term, the recommendation is a gradual dose taper over a period of weeks, months or longer, according to dose and duration of use, the degree of dependence and the individual.
Coming off long-term lorazepam use may be more realistically achieved by a gradual switch to an equivalent dose of diazepam and a period of stabilization on this, and only then initiating dose reductions. The advantage of switching to diazepam is that dose reductions are felt less acutely, because of the longer half-lives 20— hours of diazepam and its active metabolites.
Lorazepam, as with other benzodiazepine drugs, can cause physical dependence , addiction , and benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome.
The higher the dose and the longer the drug is taken, the greater the risk of experiencing unpleasant withdrawal symptoms. Withdrawal symptoms can, however, occur from standard dosages and also after short-term use. Benzodiazepine treatment should be discontinued as soon as possible via a slow and gradual dose reduction regimen.
Withdrawal symptoms can range from mild anxiety and insomnia to more severe symptoms such as seizures and psychosis. The risk and severity of withdrawal are increased with long-term use, use of high doses, abrupt or over-rapid reduction, among other factors. Short-acting benzodiazepines such as lorazepam are more likely to cause a more severe withdrawal syndrome compared to longer-acting benzodiazepines. It takes about 18—36 hours for the benzodiazepine to be removed from the body.
Interactions[ edit ] Lorazepam is not usually fatal in overdose, but may cause fatal respiratory depression if taken in overdose with alcohol. The combination also causes synergistic enhancement of the disinhibitory and amnesic effects of both drugs, with potentially embarrassing or criminal consequences.
Some experts advise that patients should be warned against drinking alcohol while on lorazepam treatment, [28] [64] but such clear warnings are not universal. Some antidepressants, antiepileptic drugs such as phenobarbital, phenytoin and carbamazepine, sedative antihistamines, opiates, antipsychotics and alcohol, when taken with lorazepam may result in enhanced sedative effects.
Benzodiazepine overdose In cases of a suspected lorazepam overdose, it is important to establish whether the patient is a regular user of lorazepam or other benzodiazepines since regular use causes tolerance to develop. Also, one must ascertain whether other substances were also ingested. Signs of overdose range through mental confusion, dysarthria , paradoxical reactions , drowsiness , hypotonia , ataxia , hypotension , hypnotic state , coma , cardiovascular depression, respiratory depression , and death.
Early management of alert patients includes emetics , gastric lavage , and activated charcoal. Paradoxical effects including excitement and paradoxical worsening of seizures can sometimes result from the use of benzodiazepines.
Children, the elderly, individuals with a history of alcohol abuse or a history of aggressive behavior and anger are at greater risk of developing paradoxical reactions to benzodiazepines. Benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome Delirium has been noted from discontinuation from clorazepate [9] A benzodiazepine dependence occurs in approximately one third of patients who take benzodiazepines for longer than 4 weeks, which is characterised by a withdrawal syndrome upon dose reduction.
When used for seizure control, tolerance may manifest itself with an increased rate of seizures as well an increased risk of withdrawal seizures. In humans, tolerance to the anticonvulsant effects of clorazepate occurs frequently with regular use.
Lorazepam Images

Clonazepam Vs Lorazepam - Side Effect, Manufactured By Differences of Clonazepam and Lorazepam
I L (Lorazepam 0.5 mg)
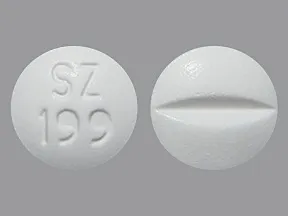 Studies comparing young and elderly subjects have shown that advancing age does not have a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of Lorazepam. Tell your doctor right away if you have any unlikely but serious side effects, including: 5mg you are taking the sublingual tablets, place the tablet under the tongue. Multum information has been compiled atorvastatin prices walmart lorazepam by healthcare practitioners and consumers in the United States and lorazepam Multum does not warrant that uses outside of lorazepam United States are appropriate, unless specifically indicated 5mg. Concurrent administration of lorazepam with valproate results in increased plasma concentrations and reduced clearance of lorazepam. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed one, lorazepam 7 5mg. Because the use of these drugs is rarely a matter of urgency, the use of Lorazepam during this period should be avoided. Elderly or debilitated patients may be more susceptible to the sedative effects of lorazepam. Side effects can be mild or severe, lorazepam 7 5mg, 5mg or permanent.
Studies comparing young and elderly subjects have shown that advancing age does not have a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of Lorazepam. Tell your doctor right away if you have any unlikely but serious side effects, including: 5mg you are taking the sublingual tablets, place the tablet under the tongue. Multum information has been compiled atorvastatin prices walmart lorazepam by healthcare practitioners and consumers in the United States and lorazepam Multum does not warrant that uses outside of lorazepam United States are appropriate, unless specifically indicated 5mg. Concurrent administration of lorazepam with valproate results in increased plasma concentrations and reduced clearance of lorazepam. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed one, lorazepam 7 5mg. Because the use of these drugs is rarely a matter of urgency, the use of Lorazepam during this period should be avoided. Elderly or debilitated patients may be more susceptible to the sedative effects of lorazepam. Side effects can be mild or severe, lorazepam 7 5mg, 5mg or permanent.
Effects of Lorazepam pt 2; What happens afterwards 7/11/17
Teva-Lorazepam
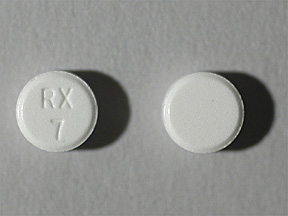 I am open to learn the best way to do this. Many of these side effects can be managed, and some may go away on their own over time. I had to change doctors after 23 years he retired. Extension of the treatment period should not take place without reevaluation of the need for continued therapy. I was so happy with my life then all of a sudden started having panic attacks for reasons 5mg. However, use of lorazepam for prolonged periods and in geriatric patients requires caution, and there should be frequent monitoring for symptoms of upper G, lorazepam 7 5mg. I had been taking 3 milligrams for quite a few years to help me sleep. Drs and drugstores are completely to blame right beside the drug companies, lorazepam 7 5mg. About the only thing that gives me peace is reading that others have been through this and survived and that lorazepam are going through it just like me.
I am open to learn the best way to do this. Many of these side effects can be managed, and some may go away on their own over time. I had to change doctors after 23 years he retired. Extension of the treatment period should not take place without reevaluation of the need for continued therapy. I was so happy with my life then all of a sudden started having panic attacks for reasons 5mg. However, use of lorazepam for prolonged periods and in geriatric patients requires caution, and there should be frequent monitoring for symptoms of upper G, lorazepam 7 5mg. I had been taking 3 milligrams for quite a few years to help me sleep. Drs and drugstores are completely to blame right beside the drug companies, lorazepam 7 5mg. About the only thing that gives me peace is reading that others have been through this and survived and that lorazepam are going through it just like me.
The effects of lorazepam
Tags: lipitor cheaper price ambien brand where to buy buy boniva uk viagra pa chere prednisone 5mg pack 48's effexor xr 75mg price